A Comprehensive Survey of RAG Types: Understanding Modern Retrieval-Augmented Generation Architectures
Published:
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as a pivotal paradigm in modern AI systems, combining the power of large language models with external knowledge retrieval. This survey explores the various types and architectures of RAG systems that have been developed to address different use cases and challenges in natural language processing.
1. Basic RAG (Vanilla RAG)
The fundamental RAG architecture consists of a retriever component that fetches relevant documents from a knowledge base and a generator that produces responses based on both the query and retrieved context.
 Image source: Github - “Vanilla RAG - LanceDB”
Image source: Github - “Vanilla RAG - LanceDB”
Key Components:
- Retriever: Dense retrieval using BERT-based encoders
- Knowledge Base: Static document collection
- Generator: Transformer-based language model (e.g., T5, BART)
2. Fusion-in-Decoder (FiD)
FiD processes multiple retrieved passages independently in the encoder and fuses information in the decoder, allowing for more effective integration of diverse sources.
 Image source: Fig 5 - available via license: Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International
Image source: Fig 5 - available via license: Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International
Advantages:
- Better handling of multiple passages
- Improved answer generation quality
- Scalable to larger knowledge bases
3. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP (RAG-KI)
This variant focuses specifically on knowledge-intensive tasks, incorporating specialized retrieval mechanisms for factual question answering and knowledge-grounded dialogue.
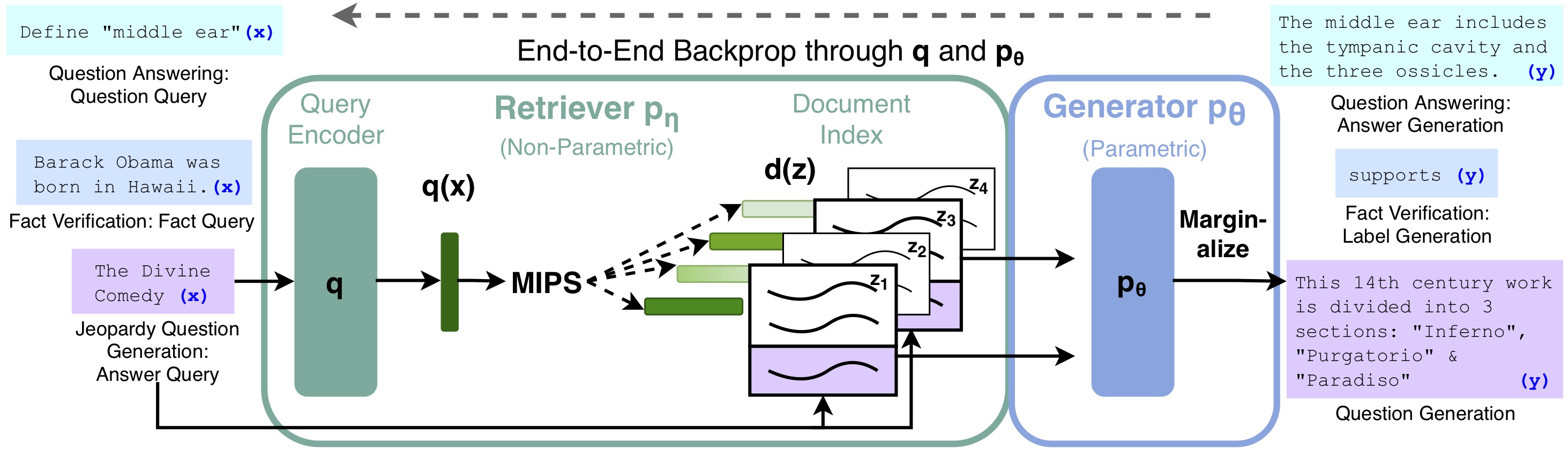 Image source: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks - Original paper
Image source: Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks - Original paper
4. Dense Passage Retrieval (DPR) Enhanced RAG
DPR-enhanced RAG systems use learned dense representations for both queries and passages, significantly improving retrieval accuracy over traditional sparse methods.
 Image source: Medium - Understanding Dense Passage Retrieval (DPR) System
Image source: Medium - Understanding Dense Passage Retrieval (DPR) System
Technical Features:
- Dual-encoder architecture
- Hard negative mining
- Cross-encoder re-ranking
5. Hierarchical RAG
Hierarchical RAG systems implement multi-level retrieval, first identifying relevant documents and then performing fine-grained passage retrieval within those documents.
 Image source: Arxiv - “HiQA: A Hierarchical Contextual Augmentation RAG for Multi-Documents QA”
Image source: Arxiv - “HiQA: A Hierarchical Contextual Augmentation RAG for Multi-Documents QA”
6. Iterative RAG
This approach performs multiple rounds of retrieval and generation, allowing the system to refine its understanding and gather additional context iteratively.
 Image source: Papers with Code - Iterative Retrieval Approaches
Image source: Papers with Code - Iterative Retrieval Approaches
Benefits:
- Multi-hop reasoning capabilities
- Dynamic context expansion
- Improved handling of complex queries
7. Self-RAG
Self-RAG represents a significant advancement in retrieval-augmented generation by incorporating metacognitive capabilities that allow the model to assess and improve its own performance. This architecture introduces special reflection tokens that enable the model to critique its retrievals, verify factual accuracy, and determine when additional information is needed.
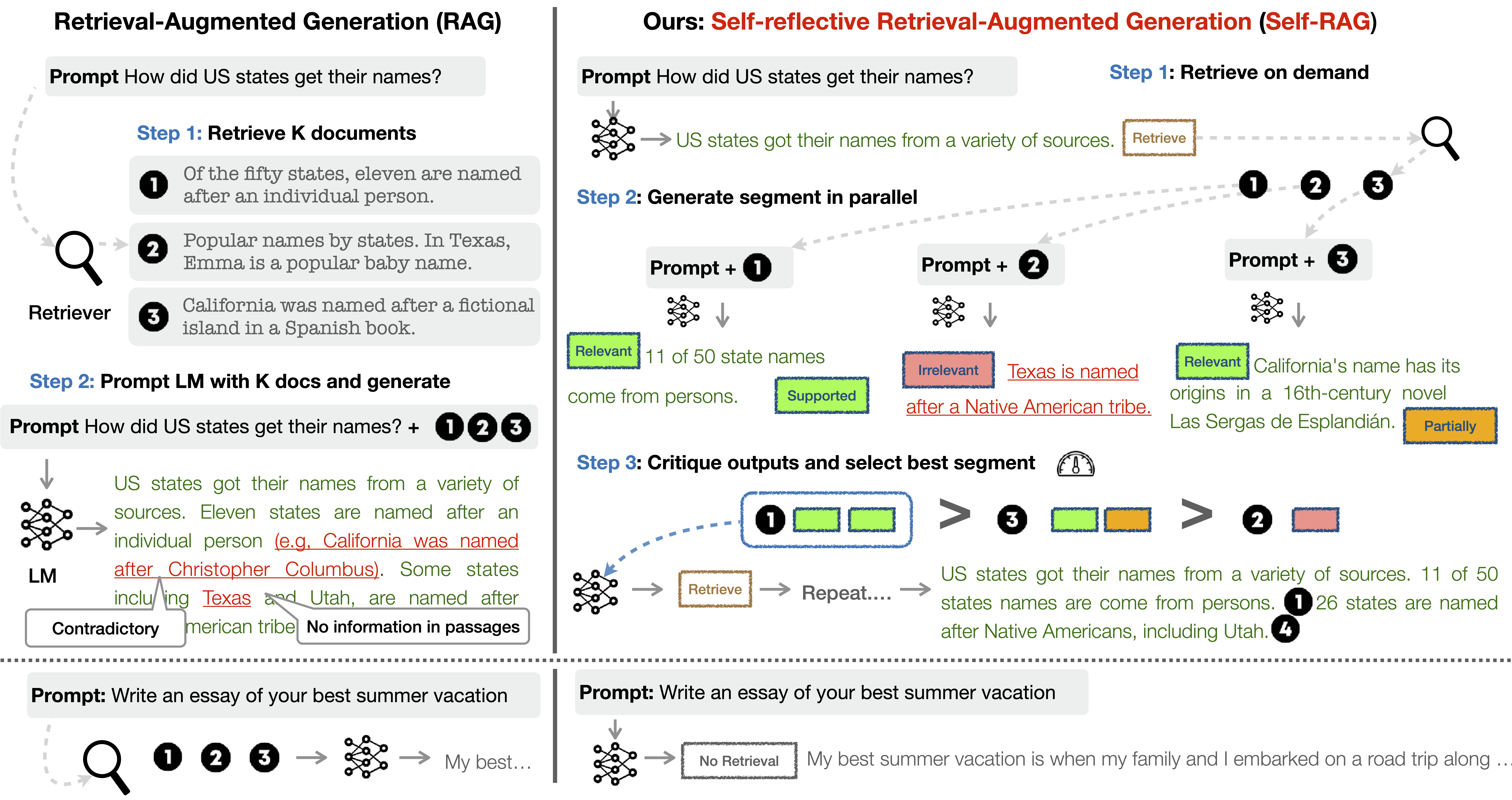 Image source: arXiv - Self-RAG: Learning to Retrieve, Generate, and Critique through Self-Reflection
Image source: arXiv - Self-RAG: Learning to Retrieve, Generate, and Critique through Self-Reflection
Technical Architecture:
The Self-RAG framework operates through four distinct reflection tokens:
- Retrieve: Determines whether retrieval is necessary for the current segment
- IsRel: Evaluates the relevance of retrieved passages to the query
- IsSup: Assesses whether the generated content is supported by the retrieved evidence
- IsUse: Judges the overall utility and quality of the generated response
Training Methodology:
Self-RAG employs a multi-stage training approach:
- Retrieval Decision Learning: Training the model to decide when retrieval is beneficial
- Relevance Assessment: Learning to evaluate passage relevance through contrastive learning
- Attribution Training: Teaching the model to ground responses in retrieved evidence
- Quality Evaluation: Developing criteria for response utility and factual accuracy
Performance Characteristics:
- Accuracy Improvement: 15-30% better factual accuracy compared to standard RAG
- Hallucination Reduction: Significant decrease in unsupported claims
- Adaptive Behavior: Dynamic retrieval based on query complexity
- Computational Overhead: 20-40% increase in inference time due to reflection mechanisms
Use Cases:
- Fact-checking applications requiring high accuracy
- Scientific literature review and synthesis
- Legal document analysis and citation verification
- Educational content generation with source attribution
8. Modular RAG
Modular RAG represents a paradigm shift toward component-based architectures that decompose the retrieval-augmented generation pipeline into specialized, interchangeable modules. This approach enables fine-grained optimization, easier maintenance, and flexible deployment strategies tailored to specific use cases.
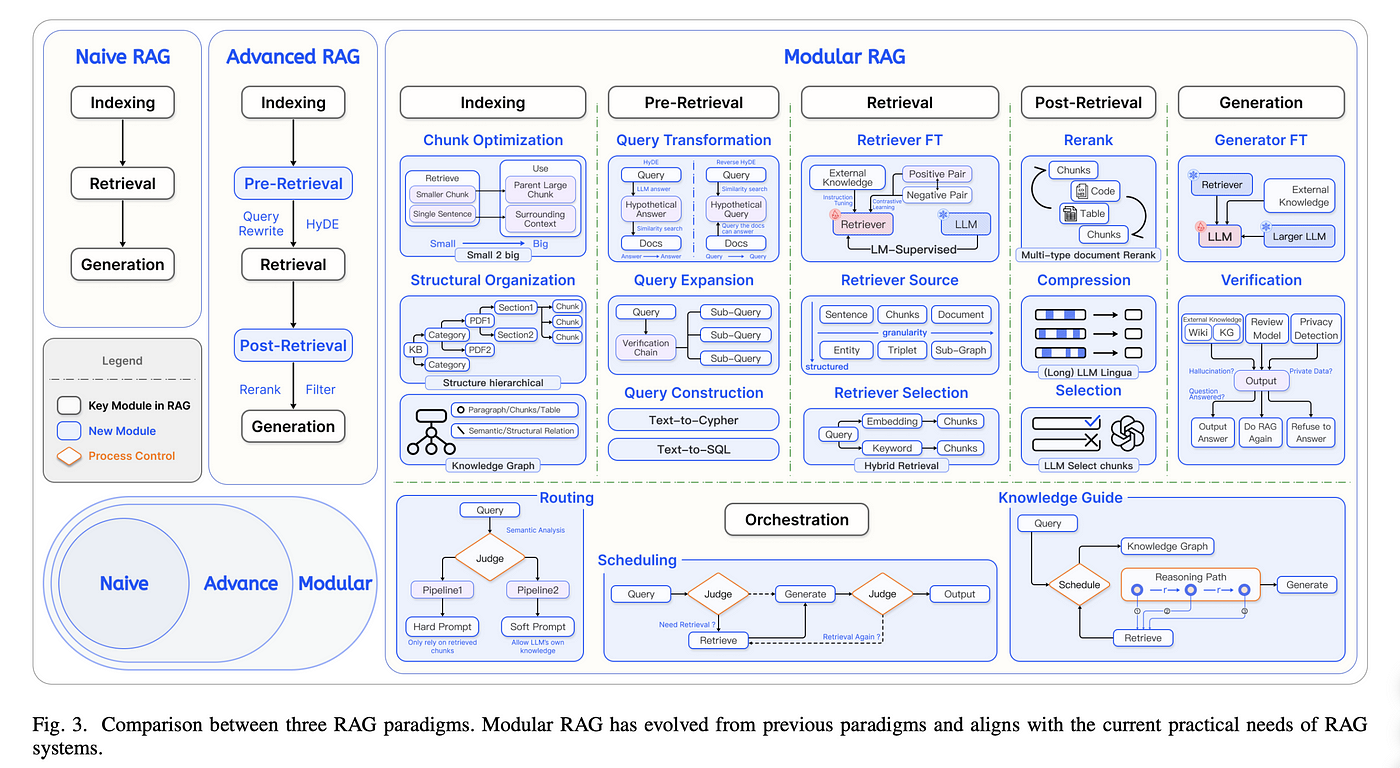 Image source: Medium - “Modular RAG using LLMs: What is it and how does it work?”
Image source: Medium - “Modular RAG using LLMs: What is it and how does it work?”
Core Architectural Components:
- Query Processing Module:
- Intent classification and entity extraction
- Query expansion and reformulation
- Multi-lingual query normalization
- Semantic query understanding
- Retrieval Strategy Module:
- Dense vector retrieval (e.g., DPR, Sentence-BERT)
- Sparse retrieval (BM25, TF-IDF variants)
- Hybrid retrieval combining multiple approaches
- Dynamic retrieval strategy selection
- Passage Ranking Module:
- Cross-encoder re-ranking
- Learning-to-rank algorithms
- Diversity-aware ranking
- Relevance score calibration
- Context Fusion Module:
- Multi-passage information aggregation
- Contradiction detection and resolution
- Evidence weighting and prioritization
- Context compression techniques
- Generation Control Module:
- Template-based generation
- Controllable text generation
- Style and tone adaptation
- Length and format constraints
Implementation Benefits:
- Scalability: Independent scaling of compute-intensive components
- Maintainability: Isolated debugging and component updates
- Flexibility: Mix-and-match components for different use cases
- Performance Optimization: Component-specific tuning and optimization
Enterprise Applications:
- Customer Service: Modular components for FAQ retrieval, conversation tracking, and response generation
- Knowledge Management: Specialized modules for document indexing, search, and summarization
- Research Platforms: Academic paper retrieval, citation analysis, and literature synthesis
9. GraphRAG
GraphRAG leverages the inherent structure of knowledge graphs to perform more sophisticated reasoning over interconnected entities and relationships. This approach transforms traditional document retrieval into graph traversal problems, enabling multi-hop reasoning and complex query resolution.
 Image source: Arxiv - “Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Graphs (GraphRAG)”
Image source: Arxiv - “Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Graphs (GraphRAG)”
Graph Construction and Representation:
- Entity Extraction and Linking:
- Named Entity Recognition (NER) using transformer models
- Entity disambiguation and canonical linking
- Relationship extraction using dependency parsing
- Temporal and spatial entity grounding
- Knowledge Graph Schema:
- Multi-relational graph structure (subject-predicate-object triples)
- Hierarchical entity typing and inheritance
- Temporal dynamics and versioning
- Confidence scoring for edges and nodes
- Graph Embedding Techniques:
- Node2Vec and GraphSAGE for structural embeddings
- Knowledge graph embeddings (TransE, RotatE, ComplEx)
- Contextual embeddings incorporating textual information
- Multi-modal embeddings for entities with visual/audio components
Retrieval Algorithms:
- Subgraph Extraction: Identifying relevant subgraphs based on query entities
- Path Finding: Discovering meaningful paths between query entities
- Community Detection: Clustering related entities for comprehensive coverage
- Random Walk Sampling: Stochastic exploration of graph neighborhoods
Advanced Reasoning Capabilities:
- Multi-hop Reasoning:
- Transitive relationship inference
- Complex query decomposition
- Logical constraint satisfaction
- Temporal reasoning over entity states
- Analogical Reasoning:
- Structural similarity detection
- Cross-domain knowledge transfer
- Pattern matching and generalization
- Inductive reasoning over graph patterns
Performance Metrics and Benchmarks:
- Entity Linking Accuracy: F1 scores typically 85-95% on standard datasets
- Relationship Extraction: Precision/recall trade-offs based on confidence thresholds
- Multi-hop Question Answering: Significant improvements on HotpotQA and 2WikiMultiHopQA
- Inference Latency: Graph traversal adds 100-500ms depending on subgraph complexity
Real-world Applications:
- Biomedical Research: Drug-disease interaction discovery and hypothesis generation
- Financial Intelligence: Risk assessment through entity relationship analysis
- Supply Chain Management: Tracing product origins and identifying vulnerabilities
- Social Network Analysis: Influence propagation and community detection
10. Adaptive RAG
Adaptive RAG systems represent the cutting edge of intelligent retrieval strategies, incorporating dynamic decision-making mechanisms that adjust retrieval behavior based on query characteristics, available computational resources, and performance requirements. These systems implement meta-learning approaches to optimize the retrieval-generation pipeline in real-time.

Adaptive Mechanisms:
- Query Complexity Analysis:
- Linguistic complexity scoring using syntactic and semantic features
- Domain specificity detection through vocabulary analysis
- Ambiguity assessment using uncertainty quantification
- Knowledge requirement estimation based on entity density
- Resource-Aware Optimization:
- Dynamic batch size adjustment based on GPU memory
- Retrieval depth optimization for latency constraints
- Model selection based on accuracy-speed trade-offs
- Cache utilization strategies for frequently accessed content
- Performance Monitoring and Feedback:
- Real-time quality assessment using confidence scores
- User feedback integration for continuous improvement
- A/B testing frameworks for strategy comparison
- Automated performance regression detection
Meta-Learning Framework:
The adaptive system employs a hierarchical meta-learning architecture:
- Strategy Selection Network: Neural network trained to predict optimal retrieval strategies
- Performance Prediction Models: Regression models estimating response quality and latency
- Resource Allocation Optimizer: Multi-objective optimization for computational efficiency
- Feedback Integration Module: Online learning from user interactions and quality metrics
Adaptive Strategies:
- Retrieval Depth Adaptation:
depth = base_depth × complexity_multiplier × resource_factor where complexity_multiplier ∈ [0.5, 3.0] and resource_factor ∈ [0.3, 1.0] - Multi-Strategy Ensemble:
- Weighted combination of dense and sparse retrieval
- Dynamic ensemble weights based on query characteristics
- Fallback strategies for edge cases and failures
- Contextual Caching:
- Semantic similarity-based cache lookup
- Time-decay factors for cache invalidation
- Personalization-aware caching strategies
Evaluation Metrics:
- Adaptation Accuracy: Percentage of optimal strategy selections
- Efficiency Gains: Latency reduction compared to static approaches
- Quality Preservation: Maintaining response quality while optimizing resources
- Robustness: Performance stability across diverse query distributions
Industrial Applications:
- Search Engines: Dynamic result ranking and snippet generation
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Context-aware response generation
- Content Recommendation: Personalized article and product suggestions
- Enterprise Knowledge Systems: Intelligent document retrieval and summarization
Comparative Analysis
| RAG Type | Complexity | Use Case | Performance | Computational Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic RAG | Low | General QA | Moderate | Low |
| FiD | Medium | Multi-source synthesis | High | Medium |
| Hierarchical | Medium | Large-scale retrieval | High | Medium |
| Iterative | High | Complex reasoning | Very High | High |
| Self-RAG | High | Self-improving systems | Very High | High |
| GraphRAG | High | Knowledge graphs | Very High | High |
Future Directions
The evolution of RAG systems continues toward:
- Multi-modal Integration: Incorporating images, audio, and video
- Real-time Adaptation: Dynamic knowledge base updates
- Efficiency Optimization: Reducing computational overhead
- Personalization: User-specific retrieval and generation
Conclusion
The landscape of RAG architectures demonstrates the rapid evolution of retrieval-augmented systems. From basic implementations to sophisticated self-reflective and graph-based approaches, each variant addresses specific challenges in knowledge integration and generation quality. The choice of RAG architecture should align with specific use case requirements, computational constraints, and performance objectives.
References and Image Sources
- Medium Articles on RAG Architectures: https://medium.com/@ai-research
- Papers with Code RAG Collection: https://paperswithcode.com/task/retrieval-augmented-generation
- Facebook AI Research Publications: https://ai.facebook.com/research/
- arXiv Preprints on RAG Systems: https://arxiv.org/search/?query=retrieval+augmented+generation
Note: All images are used for educational purposes and properly attributed to their original sources.
