Qdrant vs Milvus: Which Vector Database is Right for You?
Published:
Vector databases store data as vectors (lists of numbers) instead of using traditional rows and columns. They use high-dimensional vector embeddings to handle unstructured data like text, images, and audio much better than regular databases can.
Qdrant: What is it?
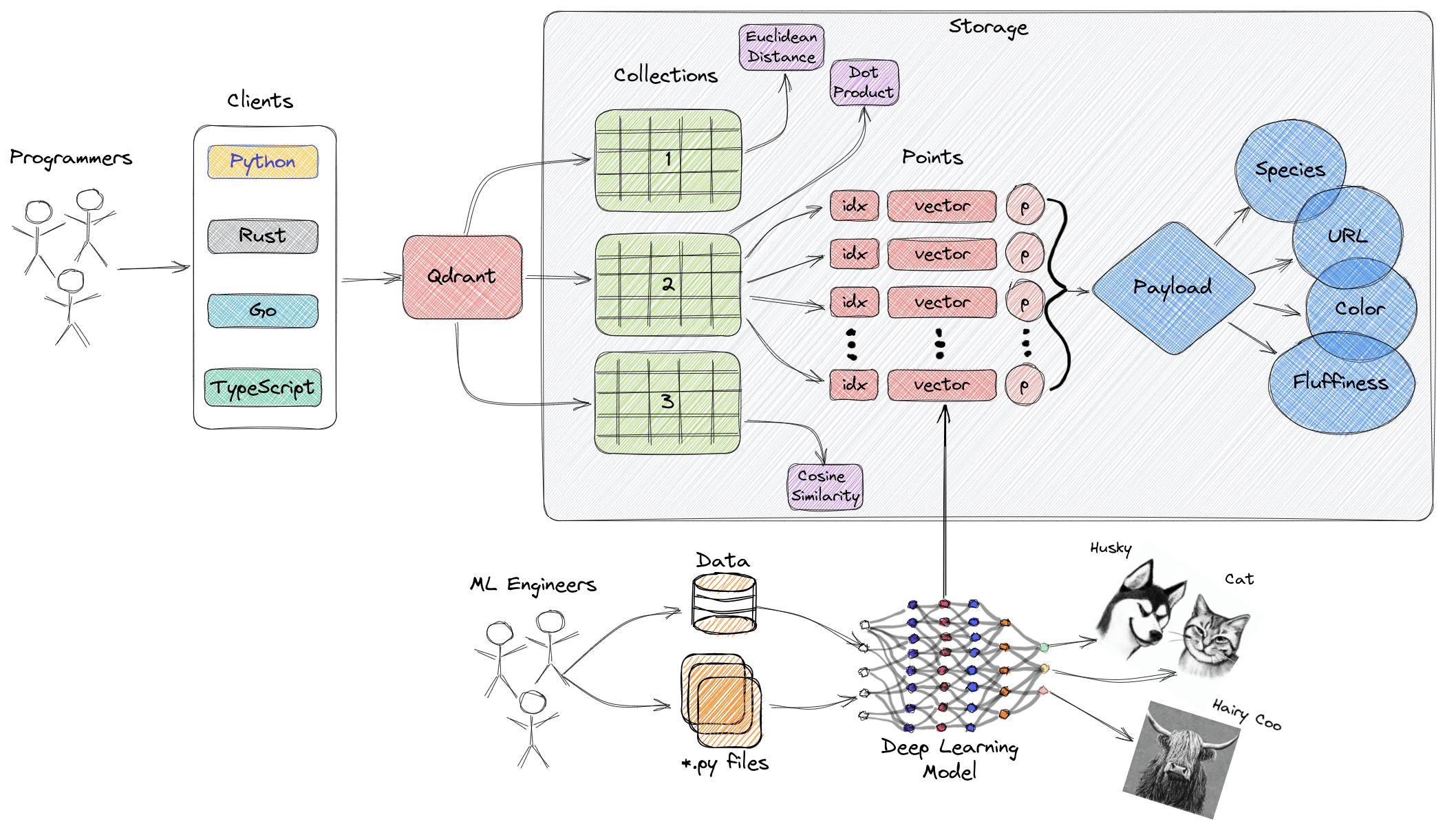
Qdrant is an open-source, cloud-native vector database. It powers search engines, recommendation systems, and machine learning models that need to find similar items quickly.
Key Features of Qdrant Vector Database
- Advanced Similarity Search: Qdrant offers multiple ways to compare vectors (dot product, cosine similarity, Euclidean distance, Manhattan distance). You can attach extra JSON data (called “payload”) to each vector.
- Built Using Rust: Qdrant is powered by Rust, making it extremely fast and memory-safe without needing garbage collection. It’s as fast as C/C++ with fewer bugs.
- Easy Scaling: Qdrant grows with your needs - both up (vertical) and out (horizontal). It uses the Raft protocol for clusters with replicas and shards, handling huge datasets without problems. You can create partitions within a single collection using payload.
- Powerful Filtering: Beyond storing JSON with vectors, Qdrant lets you filter results using keywords, full-text search, number ranges, nested filters, and even location-based searches.
- Hybrid Search: Qdrant works with both dense and sparse vectors. Sparse vectors (mostly zeros) help find exact keyword matches while dense vectors find semantically similar results. Combining them gives you the best of both worlds.
- Smart Compression: Qdrant offers three ways to shrink vector size: scalar quantization (balances accuracy and speed), binary quantization (fastest, smallest), and product quantization (highest compression for limited memory).
- Flexible Deployment: Run Qdrant locally with Docker (free), use the managed Qdrant Cloud service (scalable, easy setup), or choose Hybrid Cloud to connect your own systems with their managed service.
Milvus: What is it?
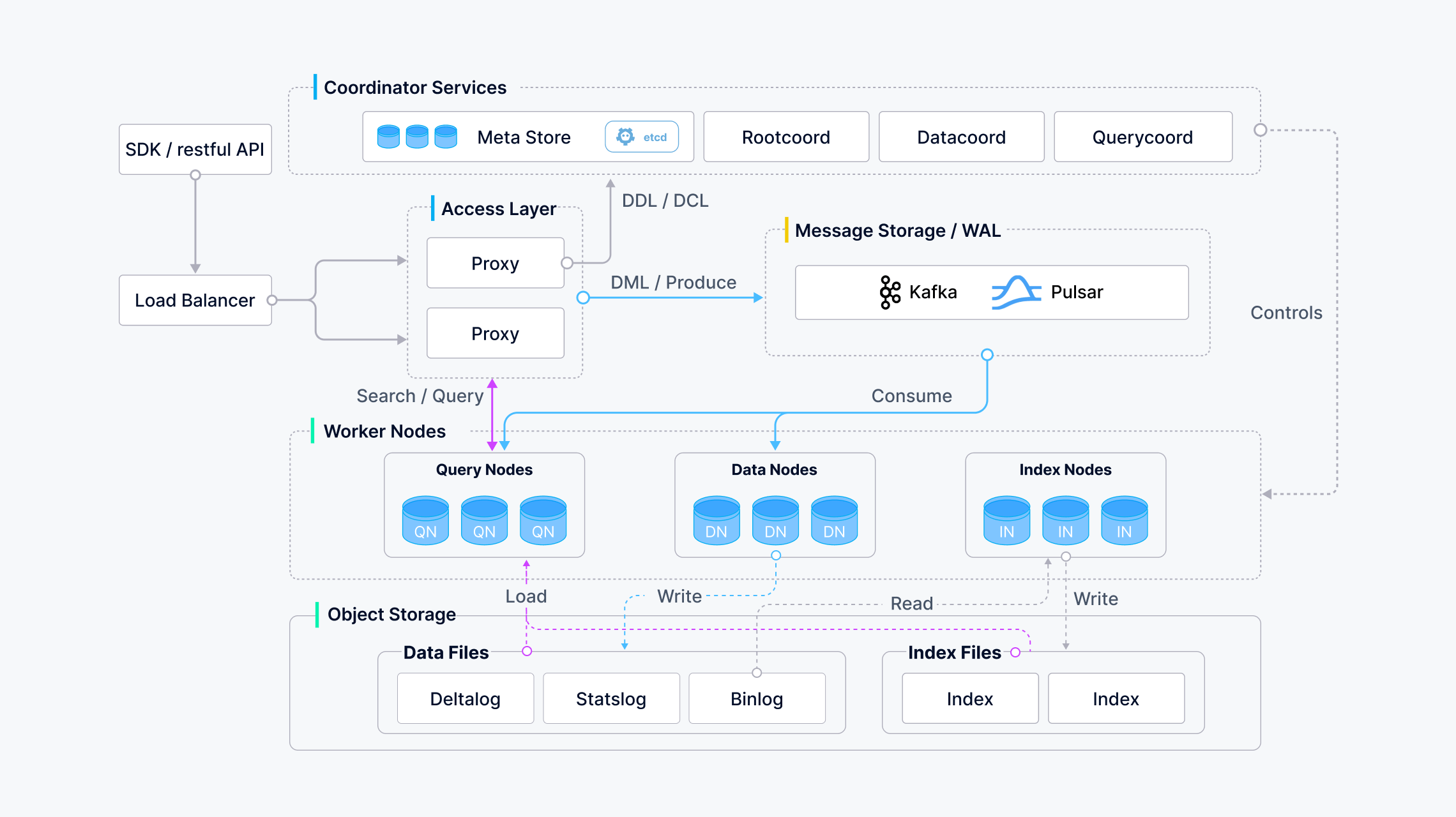
Milvus is an open-source vector database built to handle massive amounts of vector data. It’s extremely scalable and fast, supporting many different ways to search for similar vectors.

- Milvus Lite: A simple Python library you can add to your apps. Perfect for quick tests in Jupyter Notebooks or small devices with limited resources.
- Milvus Standalone: Everything packed into one Docker image for easy setup on a single machine.
- Milvus Distributed: Runs on Kubernetes clusters with a cloud-native design that can handle billions of vectors. Critical parts have backups to prevent failures.
What Makes Milvus so Fast?
- Hardware Optimization: Milvus is tuned for many different hardware setups including AVX512, SIMD, GPUs, and NVMe SSDs to get maximum speed everywhere.
- Superior Search Algorithms: Supports many search methods (IVF, HNSW, DiskANN, etc.) that have been heavily optimized. Milvus is 30%-70% faster than popular alternatives like FAISS and HNSWLib.
- C++ Search Engine: The core search engine (80% of database performance) is written in C++ for raw speed and efficient resource use. Milvus uses assembly-level optimizations and smart multi-threading to squeeze every bit of performance from your hardware.
- Column-Oriented Design: Milvus only reads the exact data it needs for a query, not entire rows. This drastically reduces data access and allows operations to work on entire columns at once, making everything much faster.
Qdrant vs Milvus: Which Vector Database is Right for You?
Both Qdrant and Milvus have unique strengths. Here’s what you need to know:
Searching and Indexing
- Text Search: Both support it, but differently. Qdrant uses full-text filtering while Milvus offers wildcard searches (like “app*” to match “apple”).
- Query Style: Qdrant keeps it simple with text-only queries. Milvus gives you more flexibility with wildcard patterns.
Multi-Vector Search
- Qdrant: Currently doesn’t support searching across multiple vector fields at once, which limits complex queries.
- Milvus: Fully supports multi-field vector searches, perfect for applications needing detailed, nuanced searching.
Speed and Growth
- Qdrant: Built for raw speed with large datasets. Its architecture is optimized for lightning-fast similarity searches, making it perfect for real-time apps.
- Milvus: Focuses on massive scale. It can handle enormous amounts of data across distributed systems without slowing down - ideal if your data will grow significantly.
Best Use Cases
- Qdrant: Perfect for apps needing fast similarity searches like recommendation engines, image search, and content discovery.
- Milvus: Ideal for complex AI applications working with multi-dimensional data and complex query needs.
Key Advantages
- Qdrant’s Filtering: Offers extremely precise filtering options to narrow down search results exactly how you need them.
- Milvus’s Indexing Options: Supports many different indexing methods (IVF, HNSW, ANNOY), giving you flexibility to choose the best approach for your specific data type and search patterns.
