A2A and MCP: What is the difference?
Published:
For developers and companies exploring AI, now is the perfect time to start learning and building. A2A and MCP together mark the beginning of a more standardized, secure approach to enterprise AI.
What is Google’s Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol?
A2A is an open protocol that lets AI agents talk to each other, no matter who made them or how. Think of it as a universal translator for AI agents from different companies and frameworks like LangChain, AutoGen, and LlamaIndex.
Google released A2A in early April 2025 at Google Cloud Next. They created it with help from over 50 technology partners, including big companies like Atlassian, Salesforce, SAP, and MongoDB. This means A2A isn’t just Google’s idea—it’s an industry-wide effort toward standardization.
At its core, A2A treats each AI agent like a networked service with a standard interface. It’s similar to how websites use HTTP to communicate, but for AI agents instead. Just like MCP solves the NxM problem, A2A makes it easy to connect different agents without writing custom code for each pair.
The Problem: Siloed Agents in a Collaborative World
Before A2A, AI agents were like islands. Each one had its own language and interface, making it hard for them to work together. It was like trying to talk to someone who speaks a different language.
Imagine this workflow:
- A customer service chatbot (Agent A, Framework X) finds a complex technical issue
- It needs to check a product knowledge base (Agent B, Framework Y) for information
- Agent B checks logs and finds a specific software version causing the problem
- It needs to contact a support agent (Agent C, Framework Z) to handle the issue
Without A2A, each agent would need custom code to talk to the others. This “silo” problem blocks innovation and limits multi-agent systems. We need agents to:
- Discover: Find other agents and know what they can do
- Communicate: Share information (text, data, files) clearly
- Coordinate: Handle tasks with multiple steps and multiple agents
- Negotiate: Agree on how to interact (text, forms, audio)
- Secure: Interact safely with proper authentication
The Solution: A2A Protocol
A2A solves these challenges by providing a standard interface. Key benefits include:
- Openness: A2A is an open protocol—anyone can implement or improve it
- Interoperability: Agents can talk regardless of their technology or vendor
- Task-Oriented: Communication uses “Tasks” for tracking work clearly
- Capability Discovery: Agents advertise their skills via standardized “Agent Cards”
- Rich Data Exchange: Supports various data types (text, JSON, forms, files)
- Flexibility: Works with different interaction patterns (request-response, streaming, webhooks)
- Security: Built-in support for authentication and authorization
A2A interaction flow
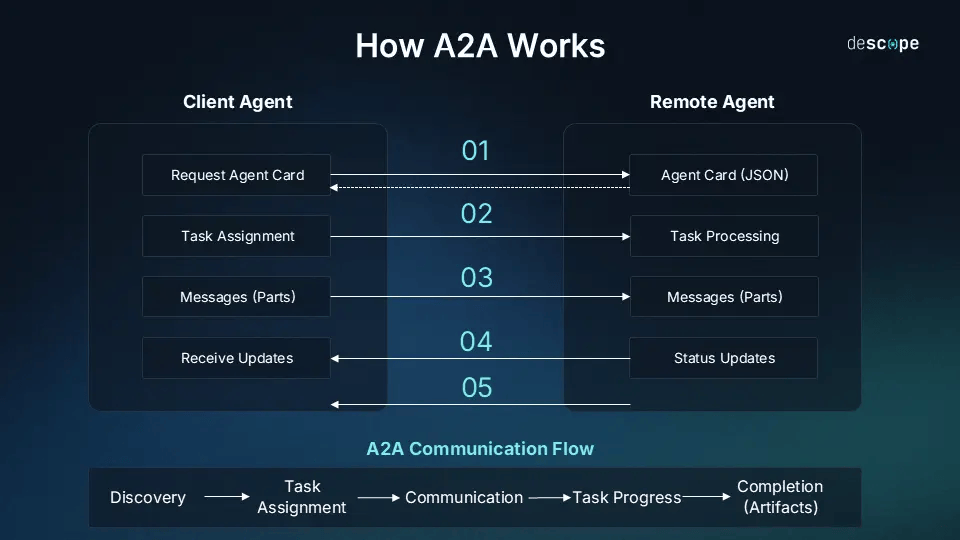
Discovery Phase: When you ask “Can you help plan my Tokyo business trip?”, your AI:
- Recognizes it needs help with flights, hotels, and activities
- Finds specialized agents for each task
- Gets their Agent Cards to check if they’re right for the job
Task Initiation: Your AI sends a job to the travel booking agent:
- Creates a request with a unique ID (POST to /taskssend)
- Includes your message: “Find flights to Tokyo May 15-20”
Processing: The booking agent can:
- Complete the task right away: “Here are your flight options”
- Ask for more details (state: input-required): “Which airline do you prefer?”
- Work on a complex task (state: working): “I’m searching for the best deals”
Multi-Turn Conversations: Agents can have back-and-forth exchanges:
- Booking agent: “Do you want direct flights only?”
- Your AI: “Yes, direct flights only”
- All messages stay within the same task ID
Status Updates: For longer tasks, A2A offers:
- Polling: Your AI checks for updates regularly
- Streaming: Agent sends live updates (Server-Sent Events)
- Push notifications: Agent sends updates to a callback URL
Task Completion: The agent finishes by:
- Marking the task as completed with results
- Marking it as failed if problems occur
- Marking it as canceled if stopped early
A2A doesn’t just let AIs chat—it lets them truly collaborate toward a common goal, creating results better than what any single agent could produce alone.
What Is MCP and How Does It Work?
MCP creates clear rules for how AI can find, connect to, and use external tools – like searching databases or running commands. This helps models do more than just use their training data, making them more flexible and aware of the world.

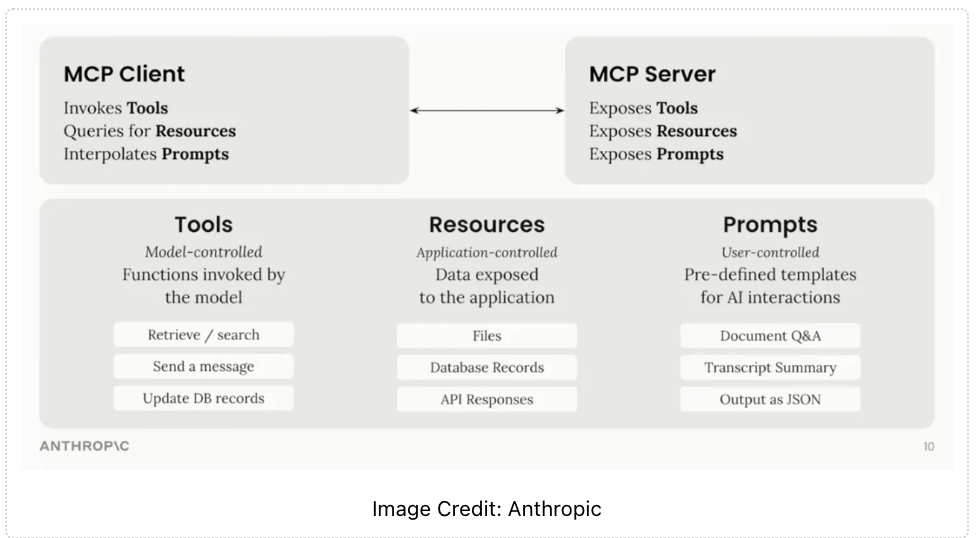
To get started with MCP:
- Install an MCP server for your tool or data. Anthropic offers ready-made servers for popular systems (Google Drive, Slack, Git, databases). Setup often needs just one command with your login details.
- Connect your AI app to the server. With Claude’s app, add servers through the interface. For custom apps, use the MCP SDK and provide the server address.
- Once connected, your AI gets new abilities from the server: tools, resources, and prompt templates.
- Start using it. Your AI can now call MCP tools when needed. Check logs to make sure connections work properly.
A2A vs. MCP: Partners, Not Rivals
A2A and MCP aren’t competing - they work together by solving different parts of the AI integration puzzle.
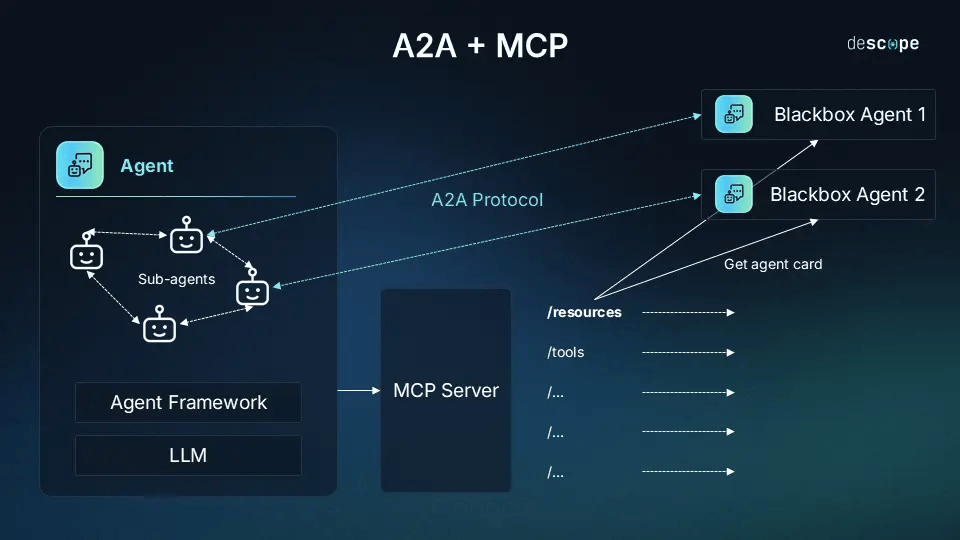
- MCP connects AI to tools (vertical integration)
- A2A connects AI to other AI (horizontal integration)
Google deliberately made A2A work with MCP. They even launched their Vertex AI agent builder with built-in MCP support the same day as A2A. This isn’t just marketing - it’s good technical design.
Think of it this way: MCP gives agents tools, A2A lets them talk while using those tools. MCP equips individual agents with abilities, while A2A helps them work as a team.
In a complete system, an agent might use MCP to get information from a database, then use A2A to send that information to another agent for analysis. Together, these protocols create better solutions for complex tasks while making development much easier.
The Future of A2A
A2A will keep improving, with plans for:
- Better security: Formal authorization and credentials in Agent Cards
- Richer interactions: Changing how agents communicate during tasks (adding audio/video)
- Faster communication: Improved streaming and notifications
The most exciting possibility is that A2A could become for AI what HTTP was for the web - a catalyst for massive innovation. As more people adopt it, we might see specialized agent teams for different industries and eventually a global network of AI agents working together.
For developers and companies exploring AI, now is the perfect time to start learning and building. A2A and MCP together mark the beginning of a more standardized, secure approach to enterprise AI.
